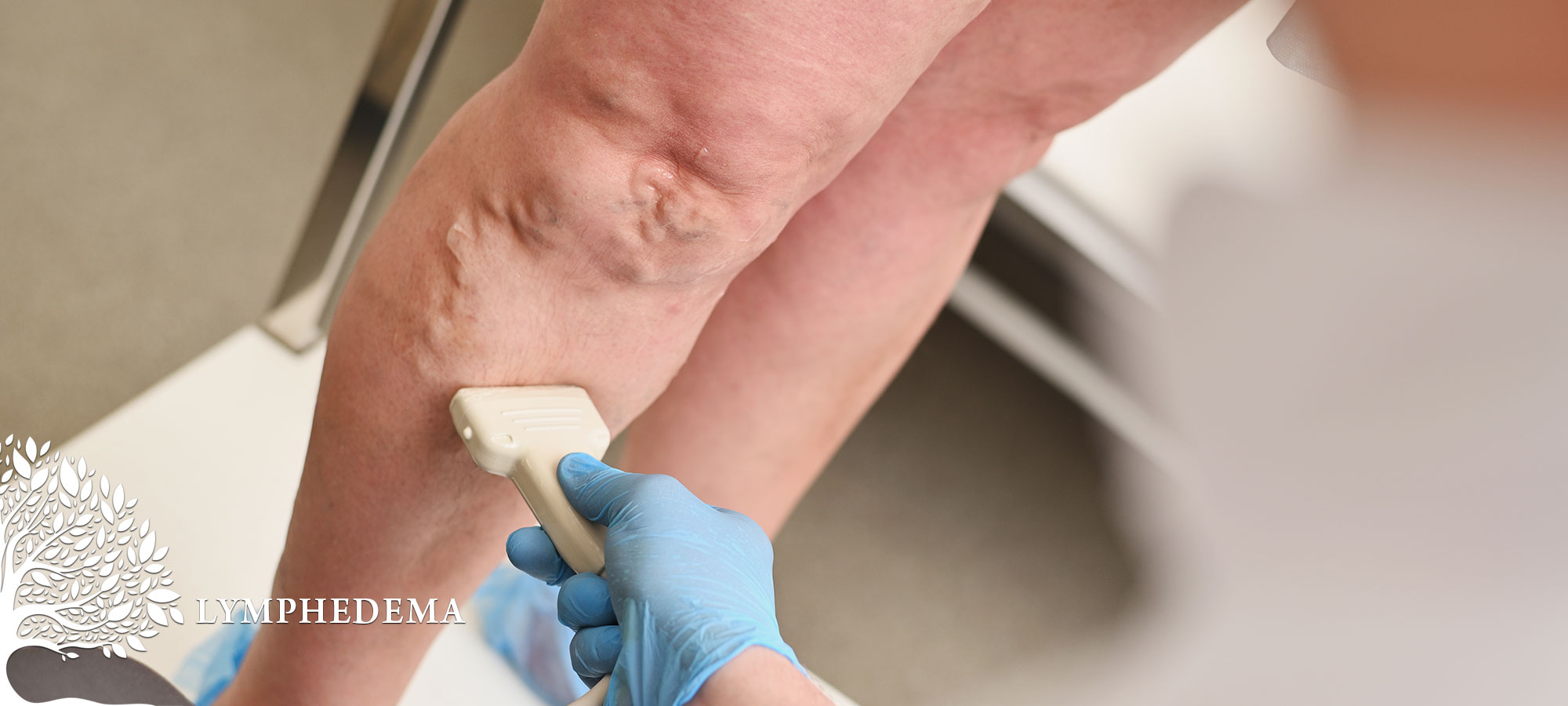
Lymphedema
Lymphedema is characterized by inadequate lymphatic fluid drainage, leading to an accumulation of lymph fluid and pronounced swelling in the limbs. In some cases, it can resemble conditions like venous blockages or heart failure.
Progression & Prognosis
Once lymphedema develops, it rarely disappears entirely. Still, effective medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and at-home care can help slow its progression and ease symptoms. Painless swelling in the affected limb often requires compression sleeves or specialized massage therapy to reduce edema.
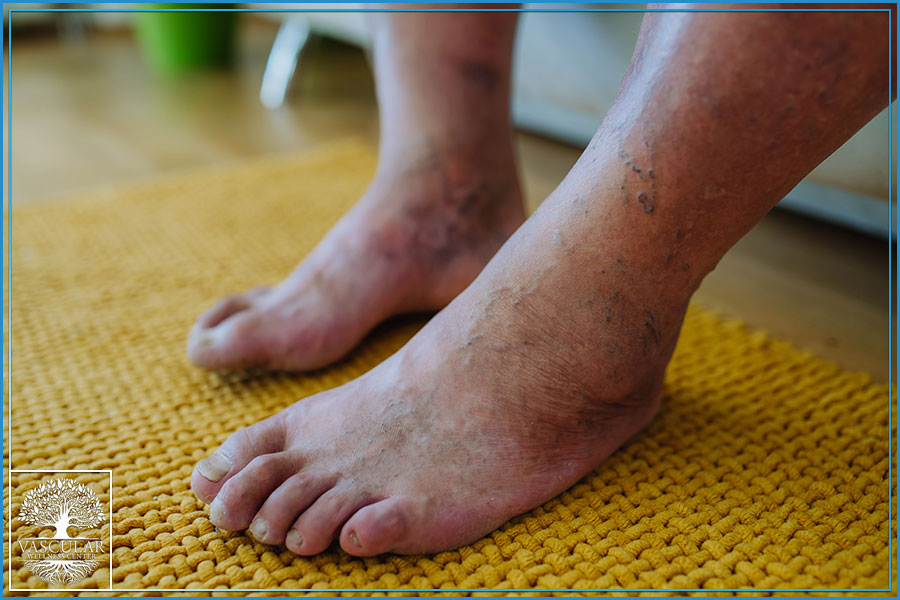
Symptoms of Lymphedema
• Swollen ankles
• Sensation of heaviness in the legs
• General leg swelling
• Fluid retention
• Redness in the legs
• Tight or tingling skin
• Skin that becomes thick or leathery
Treatments for Lymphedema
Compression Stockings
Compression stockings are an affordable, efficient way to enhance circulation in the lower limbs. By wearing them daily, patients may experience reduced swelling, improved blood flow, and a lower risk of blood clots. They can be used both short term and long term, including after surgical procedures.
Pneumatic Compression Devices
Pneumatic compression devices involve an inflatable sleeve or wrap connected to a pump. They gently inflate and deflate in cycles, mimicking a massage to promote healthy blood flow and help prevent clot formation.
Additional Treatment Options
- Massage therapy
- Exercise
- Surgery
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome Prevention
Although not all factors can be controlled, being aware of an elevated risk allows patients to take preventative steps:
• Wearing compression garments during pregnancy
• Maintaining a healthy body weight and BMI while pregnant
• Keeping a healthy BMI overall
• Regularly using compression hose
Pelvic Congestion Syndrome Treatment
Initial treatment often involves wearing compression hose or shorts to reduce pain and pressure. If this fails to provide relief, endovascular testing and therapy may be recommended. Under sedation, a venogram is performed to visualize pelvic veins. If the ovarian vein is found to be abnormally enlarged and leaking (reflux), embolization is carried out. This minimally invasive procedure involves placing a small metallic coil to close off the vein, easing pressure and pain. Key benefits of these outpatient endovascular procedures include:
• No overnight hospital stay—patients can return home the same day
• No incisions—only a needle puncture is made in the groin
• Minimal pain compared to open surgery
• Reduced risk of complications and scarring
• Significant improvement in chronic pelvic pain associated with PCS
