Reticular Veins
Reticular veins are visible veins located just beneath the skin’s surface, caused by valve dysfunction within the veins. Although they are larger than spider or telangiectasia veins, they do not protrude as varicose veins do. These veins can occasionally lead to pain or discomfort.
Progression & Prognosis
Early on, reticular veins may take on a bluish or greenish coloration, often creating a web-like pattern beneath the skin. Over time, they can enlarge and become more obvious, causing discomfort, itching, or aching sensations in the legs.
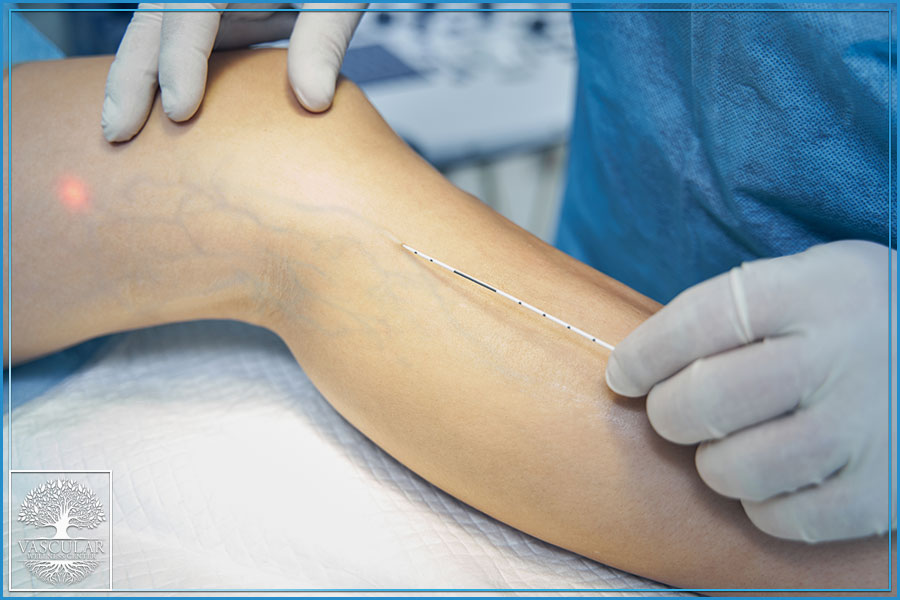
Risk Factors & Symptoms of Reticular Veins
Risk Factors
Genetic predisposition, hormonal fluctuations, obesity, and extended periods of standing can all contribute to the development of reticular veins. While they are usually less severe than varicose veins, monitoring them and addressing risk factors—either through lifestyle changes or medical treatment—can help manage their progression.
Symptoms:
- Discolored feet
- Discolored legs
- Leathery skin
- Flaky skin
- Itching
- Warmth in the legs
- Redness in the legs
Treatments for Reticular Veins
Lifestyle Changes
Early, proactive approaches can prevent reticular veins from worsening and support overall vein health.
Additional Treatments
- Varithena
- Sclerotherapy
- Phlebectomy
